Evidence of student learning includes results of assessment activities. This may include evidence of indirect (e.g. surveys) and direct (e.g. portfolio) student learning as well as institutional performance indicators (e.g. licensure pass rate).
Sample Program Assessment Reports
Click on the programs below to view completed assessment reports.
- Counseling Psychology M.Ed. Program »
- Sociology B.A. Program »
- Master of Architecture (M.Arch) Program »
- Financial Analysis and Risk Management M.S. Program »
- Music Education B.Mus Program »
- Public Health B.S. Program »
- Social Work M.S.W. Program »
- Musical Theather B.F.A. Program »
- Mechanical Engineering B.S.M.E. Program »
- Law J.D. Program »
- Media Studies and Production B.A. Program »
- Computer Science B.A. Program »
- Pharmaceutical Sciences M.S. Program »
- Podiatric Medicine DPM Program »
- Orthodontics Postdoctoral Program »
General Education Assessment Results
The General Education Program at Temple engages in a variety of direct and indirect assessment activites, including analysis of student work, analysis of GenEd syllabi and course content, and focus groups with students, faculty, and administrators.
Sample Results from General Education Program Assessment Activities:
Direct Assessment
- GenEd and the Intellectual Heritage (IH) program partnered to develop a rubric to assess ethical reasoning in the IH course sequence. The final verison of the rubric had 6 ethical reasoning competencies and an acceptable level of inter-rater reliability.
- The rubric showed that most students scored at Benchmark 1 or 2 on all 6 ethical reasoning competencies. Furthermore, students increased on 5 of the 6 competencies from the IH I course (The Good Life) to the IH II course (The Common Good).
- IH leaderhsip have developed a learning goal addressing ethical reasoning to be integrated into the IH area learning goals in line with the language of the rubric.
Indirect Assessment
- Six focus groups were held with undergraduate students to assess their GenEd experiences.
- The skills students most frequently identified developing in GenEd courses were: analytical writing, oral communication skills, critical thinking, information literacy, and critical reading.
- Some students reported that it was difficult to find GenEds that matched their interests, that larger class sizes negatively impacted their learning, and that instructors had a high impact on their experience and learning in GenEd classes.
- Based on this feedback, a course search tool was developed on the GenEd website to make it easier for students to find courses that reflect their interests. A major study of the impact of class size on student grades has been undertaken. Complaints related to inconsistencies in workload and grading schemas between different sections of the same GenEd are now being addressed through faculty development activities, the development of a data dashboard for instructors and chairs, and the inclusion of this consideration in the recertification process.
ETS Proficiency Profile Results
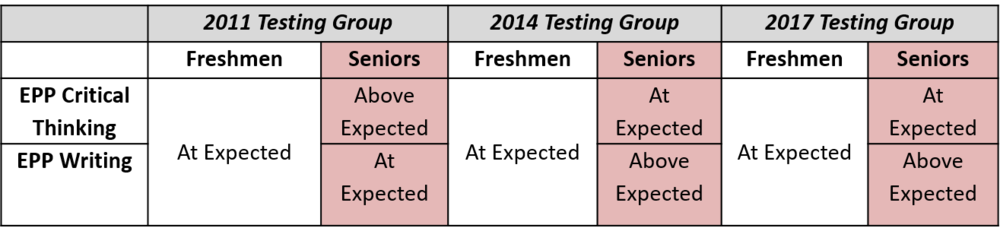
Every three years, Temple administers the ETS Proficiency Profile (EPP) to 200 freshmen and 200 seniors during the academic year to evaluate student learning gains in critical thinking and analytic writing.
- In 2016-2017, the increase in learning on analytic writing was above what would be expected at an institution testing students of similar academic abilities. In fact, this improvement in analytic writing was greater than the improvement seen at 90% of all other schools that participated in the ETS Proficiency Profile in the last 5 years.
- In 2016-2017, the increase in learning on critical thinking was at what would be expected at an institution testing students of similar academic abilities. Improvement on critical thinking was greater than the improvement seen at 70% of all other schools that participated in the past 5 years.
National Survey of Student Engagement Results
The National Survey of Student Engagement (NSSE) collects information from samples of first-year and senior students about the nature and quality of their undergraduate experience. Scores are summarized using ten engagement indicators which examine dimensions of student engagement and are organized within four themes: Academic Challenge, Learning with Peers, Experience with Faculty and Campus Environment. In 2019, Temple students scored significantly higher on most engagement indicators than students at peer insitutions. NSSE is administered every three years.
Undergraduate Retention and Graduation
Retention and graduation rates represent an important indirect measure of student learning. Temple tracks the retention and graduation of first-time full-time students using IPEDS federal reporting standards. Data regarding Temple's retention and graduation rates can be found in the annually updated Temple University Fact Book.
Student Achievement Measure
In addition to reporting retention and graduation rates using federal reporting standards (IPEDS), Temple also participates in an alternative reporting method called the Student Achievement Measure (SAM). The Student Achievement Measure is designed to be a more comprehensive way of reporting undergraduate student progress and graduation by tracking students across multiple institutions and also reporting on transfer students.
